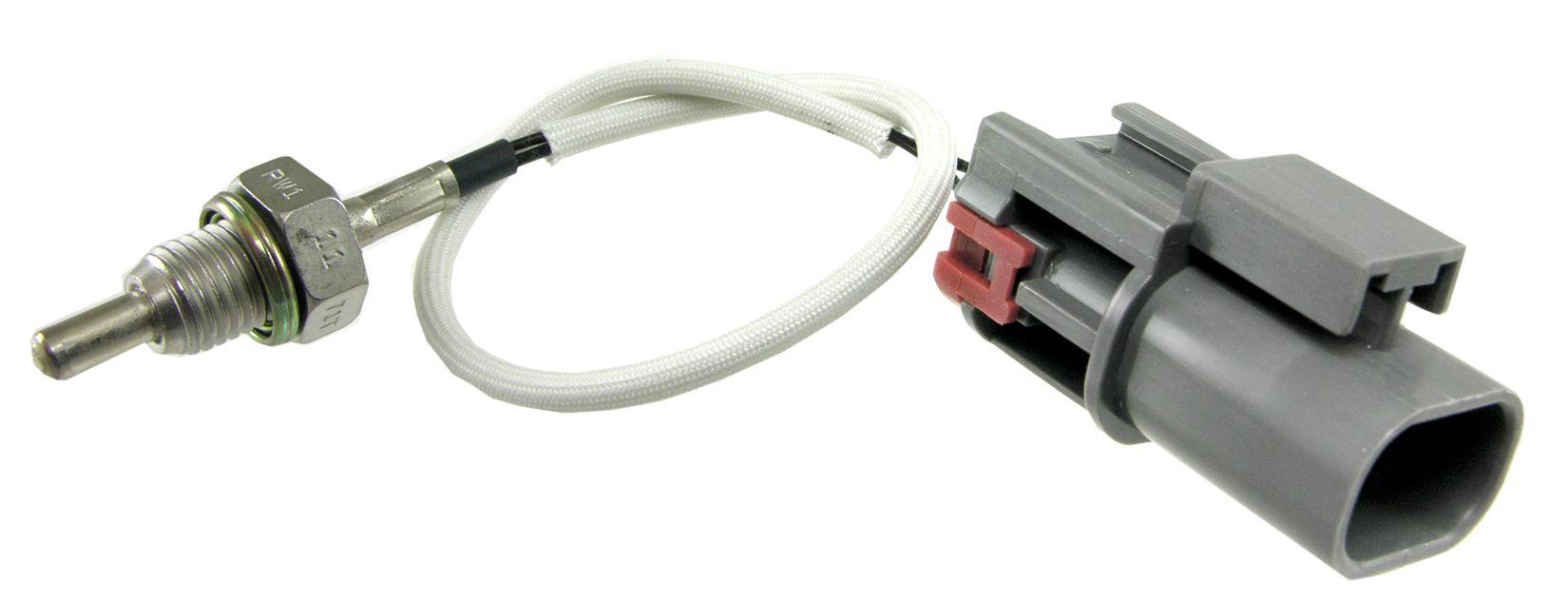
The EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) Valve Temperature Sensor is an important component in modern internal combustion engines, particularly those with EGR systems designed to reduce emissions. Here’s a detailed overview of its features, functions, and benefits:
Key Features:
- Temperature Measurement:
- The sensor measures the temperature of the exhaust gases flowing through the EGR system.
- Durable Construction:
- Designed to withstand high temperatures and harsh conditions within the engine compartment.
- Electrical Output:
- Provides real-time temperature readings, typically sending an analog or digital signal to the engine control unit (ECU).
- Integration with EGR System:
- Often located near the EGR valve, it works in conjunction with other sensors in the vehicle’s emissions control system.
Functions:
- EGR System Monitoring:
- Monitors the temperature of the exhaust gases recirculated back into the intake manifold to ensure optimal functioning of the EGR system.
- Emission Control:
- Helps the ECU adjust the EGR valve’s position based on the temperature of the exhaust gases, optimizing the amount of recirculated gas to minimize emissions.
- Engine Performance:
- By providing accurate temperature data, the sensor helps maintain the right balance of air and fuel for efficient combustion.
- Prevent Overheating:
- Alerts the ECU if the exhaust gas temperature exceeds safe operating limits, preventing potential damage to the engine.
Benefits:
- Reduced Emissions: By optimizing EGR operation, the sensor helps lower harmful nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions, contributing to compliance with environmental regulations.
- Improved Engine Efficiency: Ensures optimal combustion, which can enhance fuel economy and overall engine performance.
- Reliability: A functioning EGR valve temperature sensor contributes to the reliability of the emissions control system.
Symptoms of Failure:
- Check Engine Light: A malfunctioning sensor may trigger the check engine light.
- Increased Emissions: Poor EGR function due to sensor failure can lead to higher emissions and potential failure during emissions testing.
- Engine Performance Issues: Symptoms such as rough idling, poor acceleration, or reduced fuel efficiency may occur.
Replacement:
- Accessibility: Depending on the vehicle model, replacing the EGR valve temperature sensor may require some disassembly, but it is generally a straightforward process.
- Testing: Before replacement, it’s advisable to test the sensor for proper resistance and output to confirm its status.
Applications:
- Modern Vehicles: Commonly found in modern gasoline and diesel engines equipped with EGR systems to manage emissions.
- Heavy-Duty Engines: Also used in commercial vehicles and heavy-duty diesel engines to meet strict emission standards.
The EGR Valve Temperature Sensor plays a vital role in maintaining engine efficiency and reducing emissions, making it an essential component of modern automotive design. Regular maintenance and timely replacement are crucial for optimal vehicle performance.












There are no reviews yet.