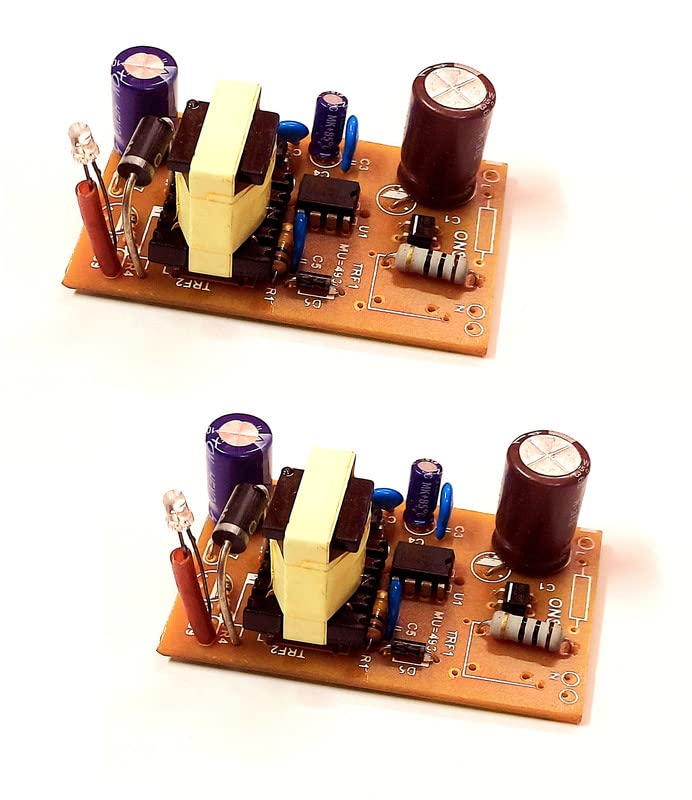
Basic Components:
- Transformer (220V AC to 12V AC): This component steps down the high 220V AC voltage to 12V AC.
- Bridge Rectifier: Converts the AC voltage from the transformer into a pulsating DC voltage.
- Smoothing Capacitor: Smooths out the rectified DC voltage by reducing ripples.
- Voltage Regulator (e.g., LM7812 or DC-DC buck converter): Ensures a steady 12V DC output.
- Fuse (Optional): Protects the circuit from overcurrent.
- Filter Capacitors: Helps to further smooth the output.
- Heat Sink (if needed): For regulating the heat dissipation of the regulator.
Step-by-Step Guide:
1. Transformer
- Choose a transformer that steps down the 220V AC to 12V AC. The transformer should be rated for at least 2A output at 12V AC. For example, a transformer rated 12V, 2A will give you 12V AC at 2A on the secondary winding.
2. Bridge Rectifier
- Use a bridge rectifier (4 diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, or a pre-made bridge rectifier module) to convert the 12V AC from the transformer into pulsating DC.
- For a 2A output at 12V DC, choose a diode bridge that can handle higher than 2A (preferably rated for at least 3A to ensure reliability and longevity).
Bridge Rectifier Setup:
- The AC input goes to the two AC terminals of the bridge rectifier.
- The positive DC output will come from the positive terminal (labeled +) of the bridge rectifier.
- The negative DC output comes from the negative terminal (labeled -) of the bridge rectifier.
3. Smoothing Capacitor
- After rectification, the DC output is pulsating (rippled). A large electrolytic capacitor (e.g., 1000µF to 2200µF rated at 25V) can be used across the DC output of the rectifier to smooth out the ripple. This capacitor helps in reducing the fluctuations in the DC voltage.
4. Voltage Regulator (LM7812 or DC-DC Converter)
- A 12V voltage regulator (e.g., LM7812 linear regulator) can be used to regulate the output and provide a stable 12V DC output.
- LM7812 is a fixed voltage linear regulator that will give you 12V DC output (it has a maximum current rating of around 1A, but this may require heatsinking if you’re drawing close to 1A).
- Note: For higher efficiency and to ensure the 2A current requirement, it’s better to use a DC-DC buck converter that can step down the voltage more efficiently. A buck converter can provide 12V DC at 2A with high efficiency, whereas linear regulators like LM7812 waste excess energy as heat.
5. Output Capacitors
- To further smooth the DC output and reduce noise, you can add smaller filter capacitors (e.g., 100nF ceramic capacitors) at the output side of the regulator or buck converter.
6. Optional Fuse
- For protection, you can add a fuse on the AC input or DC output. A 2A fuse on the DC output will prevent the circuit from damage due to overcurrent.











There are no reviews yet.